Summary
Description
What is the Chart of Accounts?
Running management reports in Sage 50 Accounts categorises your nominal accounts. This allows you to analyse your income, expenditure, assets, liabilities, and capital to assess your business performance.
The Chart of Accounts lists all nominal accounts and assigns them to these categories. You can have multiple Chart of Accounts.
 TIP: Watch our webinar recording on YouTube, where you can learn more about the chart of accounts from our expert.
TIP: Watch our webinar recording on YouTube, where you can learn more about the chart of accounts from our expert. What are nominal accounts?
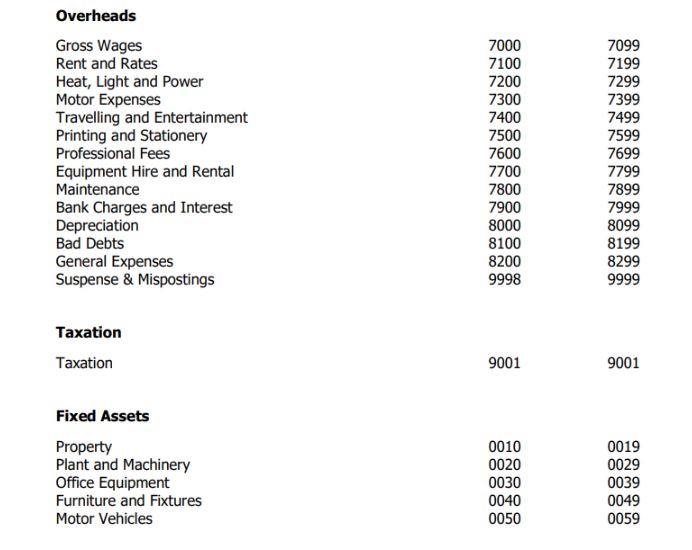
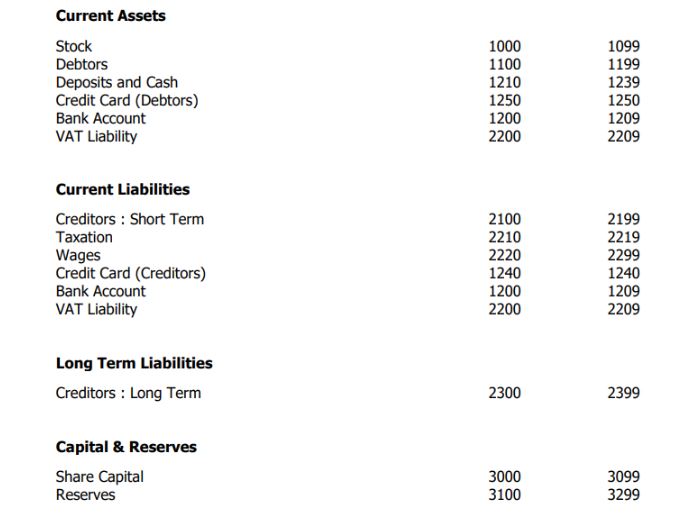
Nominal accounts track your sales and purchases, such as bank charges, petrol, or sales. Each account has a unique code, which you can customise to fit your numbering scheme.
When entering a transaction in Sage 50 Accounts, assign the relevant nominal code, such as for a sales invoice or bank payment.
Default Layout of Accounts
When setting up your company in Sage 50 Accounts, your nominal accounts and Chart of Accounts are based on the selected business type. Business types include sole trader, partnership, limited company, or charity.
What does the Chart of Accounts consist of?
The chart of accounts has two sections - Profit and Loss and Balance Sheet.
What can I do to the Chart of Accounts?
If necessary you can:
- Add, edit, or delete a chart of accounts
- Copy a chart of accounts
- Set a default chart of accounts
- Print a chart of accounts
- Send a chart of accounts details to Microsoft Excel
- Check your chart of accounts for errors
Find out how Sage HR can help
Our range of additional Sage HR modules can save time for you and your employees by simplifying HR.